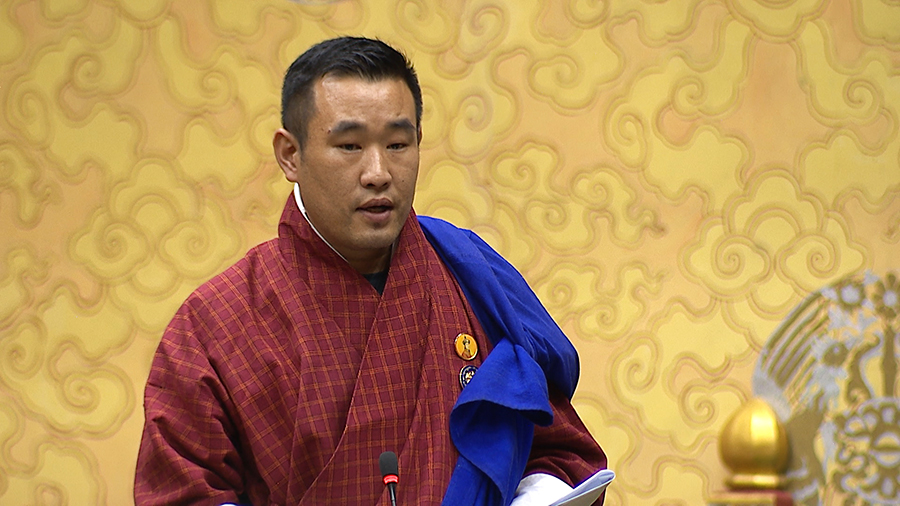
Contractors will see changes from this July, as the Finance Ministry prepares to implement revised Procurement Rules and Regulations. The reform aims to enhance transparency, competition, and efficiency in public procurement. The National Assembly unanimously supported the revised Procurement Rules and Regulations today.
Contractors will see changes from this July, as the Finance Ministry prepares to implement revised Procurement Rules and Regulations. The reform aims to enhance transparency, competition, and efficiency in public procurement. The National Assembly unanimously supported the revised Procurement Rules and Regulations today.
The member of parliament from Lamgong-Wangchang presented ten recommendations during the last session to address the challenges faced by contractors and suppliers under the 2023 Procurement Rules and Regulations.
The revised rules and regulations allow all bidders from across the country to participate in tenders issued by the district and gewog administrations. Currently, the only businesses located within the respective locality can take part in the tenders.
The revised rules also introduce stricter contractor evaluation criteria, which consider experience, performance scores, and timely project completion. Contractors found guilty of poor performance, corruption, or facing legal proceedings will face debarment from bidding for one to five years.
The Ministry of Finance is also revising the contractor scoring system to accurately reflect performance.
Other notable reforms include the allowance for joint ventures and a reduction in bid submission days to streamline the procurement process.
Since February, the Ministry has implemented several of the endorsed recommendations. Contractors are no longer required to show equipment availability during the bidding stage, instead, they can mobilise equipment as required during project execution based on the approved work plan.
Retention money will now be released to contractors in phases, providing improved cash flow during project execution.
The finance ministry has been using the electronic Government Procurement (e-GP) system since 2017 to enhance efficiency and reduce administrative burden.
The Ministry plans to introduce alternative procurement methods, such as Design, Build, Operate (DBO) method.
It will also strengthen contract management through improved supervision and monitoring mechanisms as part of its ongoing reform efforts.
Kinzang Lhadon & Sangay Chozom
Edited by Sangay Chezom